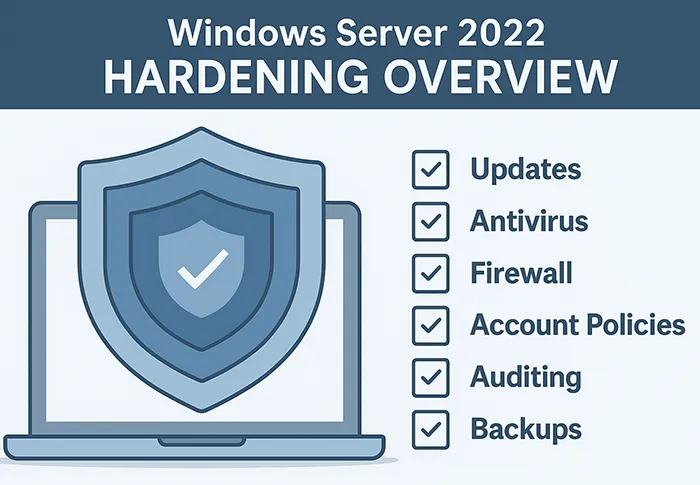
Windows Server 2022 is the backbone of many enterprise IT environments. However, if left unsecured, it becomes a prime target for ransomware, privilege escalation attacks, and data breaches. Hardening your Windows Server 2022 environment is essential for protecting business-critical applications, maintaining compliance (PCI-DSS, ISO 27001, SOC 2), and ensuring operational resilience.
This detailed Windows Server 2022 Hardening Checklist will walk you through proven security best practices with screenshots, infographics, and step-by-step instructions that every system administrator should follow.
🔐 Why Server Hardening Matters
According to Microsoft, over 60% of enterprise breaches originate from misconfigured or unpatched servers. A hardened Windows Server 2022 setup:
- Prevents unauthorized access through least privilege principles.
- Mitigates ransomware and malware risks with Defender and Firewall.
- Supports compliance with ISO 27001, SOC2, PCI-DSS, HIPAA.
- Improves resilience against insider threats and external exploits.
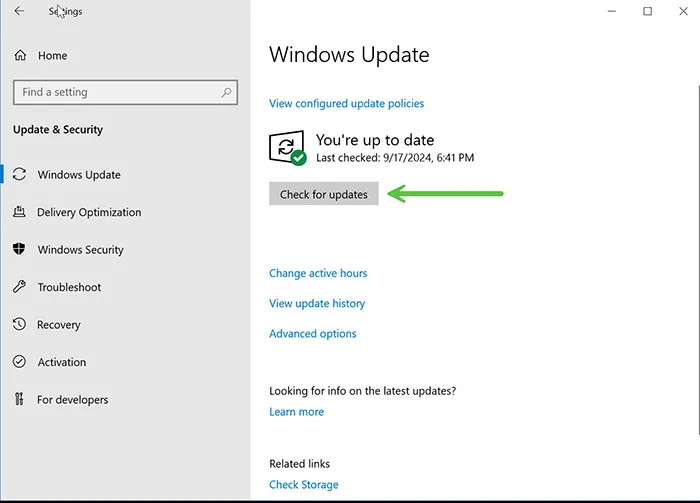
🛠️ Step 1: Keep Windows Server 2022 Updated
Patching is your first defense against known vulnerabilities. Always ensure:
- Automatic Updates: Enable automatic updates from Windows Update.
- Patch Tuesday: Apply Microsoft’s monthly updates promptly.
- Out-of-band Patches: For critical CVEs, install emergency patches immediately.
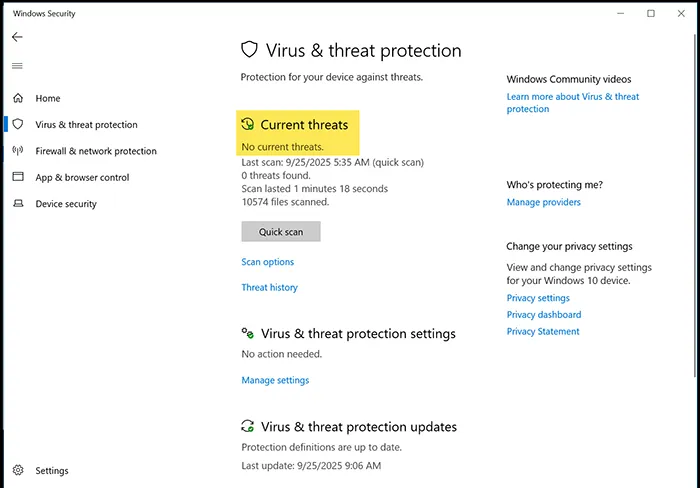
🛡️ Step 2: Enable Windows Defender & Security Baselines
Windows Defender Antivirus and Exploit Guard provide built-in protection against malware, phishing, and ransomware. Microsoft also provides Security Baseline GPOs to enforce recommended settings.
- Verify that Windows Defender Antivirus is enabled.
- Enable Cloud-delivered protection and Automatic sample submission.
- Download and apply the Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit to import baseline GPOs.
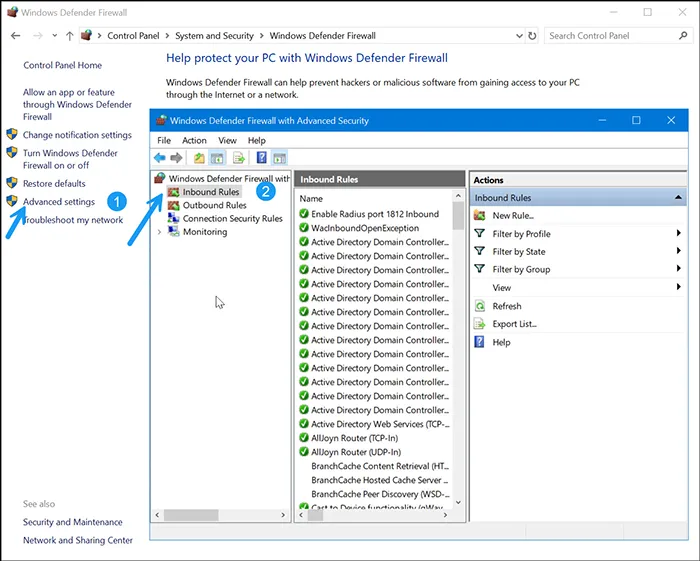
🌐 Step 3: Configure Windows Firewall
A properly configured firewall limits unnecessary exposure of services.
- Restrict inbound rules to only required ports (e.g.,
3389for RDP if needed). - Deny all traffic by default, allow only specific apps/services.
- Use IP allowlists for remote management.
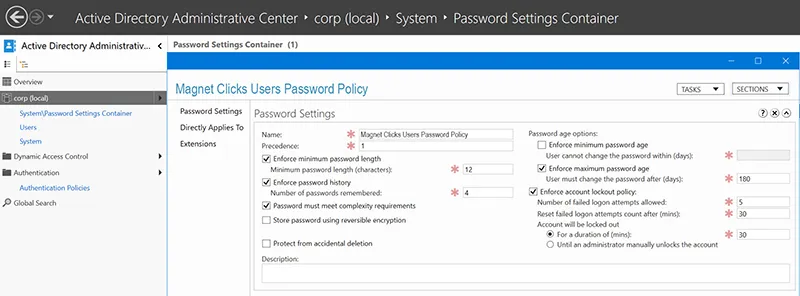
👤 Step 4: Secure Accounts & Enforce Password Policies
- Disable or rename the default Administrator account.
- Use complex passwords and enforce expiration policies.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) via ADFS or Azure AD.
- Apply Group Policy for lockout thresholds.
📊 Step 5: Enable Auditing & Logging
Monitoring is critical for detecting suspicious activity.
- Enable Advanced Audit Policy Configuration in GPO.
- Forward logs to a SIEM solution (Azure Sentinel, Splunk, etc.).
- Set alerts for failed logins, privilege escalations, and account lockouts.
🔒 Step 6: Restrict Remote Desktop (RDP)
RDP is one of the most exploited services in Windows environments. Secure it by:
- Restricting access with Network Level Authentication (NLA).
- Changing the default port (3389) to a custom port.
- Allowing access only through VPN or firewall allowlists.
💾 Step 7: Regular Backups & Disaster Recovery
- Schedule full server backups using Windows Server Backup.
- Store backups offsite or in cloud storage.
- Test recovery plans quarterly to ensure integrity.
⚠️ Step 8: Remove Unnecessary Roles & Features
Every additional feature increases the attack surface.
- Use Server Manager to uninstall unused roles (e.g., Fax, Print Services).
- Apply the principle of least privilege for all server roles.
📌 Troubleshooting Common Security Issues
- Firewall blocking apps? Check Windows Defender Firewall logs for denied connections.
- Slow server performance? Review scheduled scans and optimize backup frequency.
- ADUC not accessible? Ensure RSAT tools or AD DS roles are properly installed.
📖 See Also Related Articles
- How to Install Windows Server 2022
- How to Enable ADUC in Windows Server 2022
- How to Fix a Frozen Computer
🌐 External References
Frequently Asked Questions
Why should I harden Windows Server 2022?
Hardening reduces the attack surface, prevents unauthorized access, and helps maintain compliance with industry standards like PCI-DSS and ISO 27001.
How often should I update my Windows Server?
Check for updates at least once a week. Apply monthly cumulative updates immediately, and install emergency patches when released.
Is Windows Defender enough for server protection?
Windows Defender provides strong baseline protection, but enterprises often supplement it with SIEM tools and EDR solutions.
Should I disable RDP for better security?
If possible, yes. If RDP is required, enforce MFA, NLA, and VPN-only access.
What is the CIS Benchmark for Windows Server?
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) provides detailed configuration checklists to harden servers against common threats.